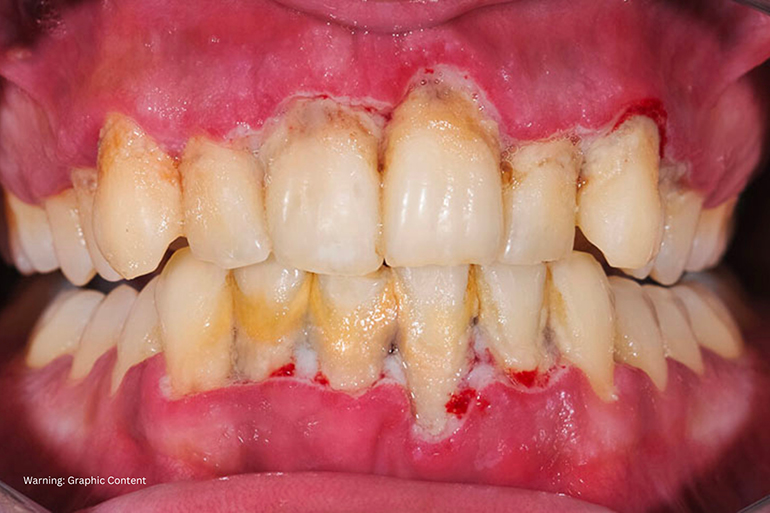
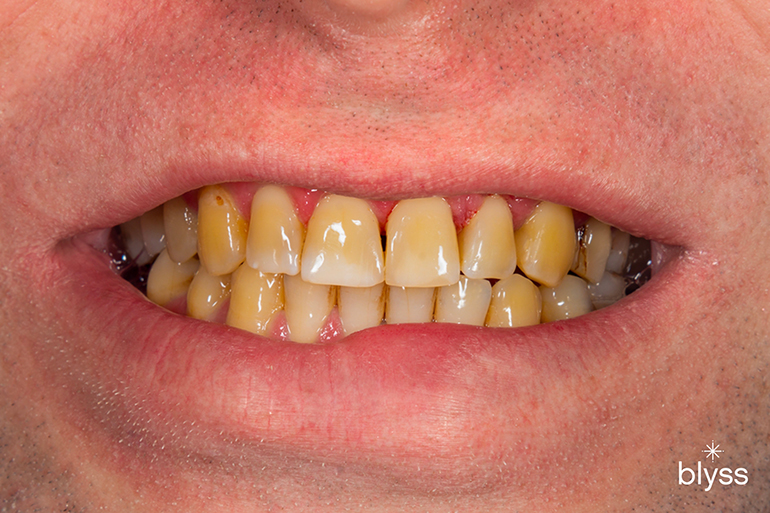
Is gum disease curable? If you’ve been diagnosed with gum disease, this is probably the first question you have in mind.
You are probably feeling a bit scared right now.
Don’t worry – you’re not alone! Gum disease is a very common condition, and there are many ways to treat it.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, almost 50% of adults have some form of periodontal disease. This is a serious issue, as gum disease can lead to tooth loss, heart disease, and other health problems.
So, what exactly is periodontal disease?
This condition is caused by a buildup of plaque and bacteria in the mouth. Over time, this plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
At the same time, gum tissue may begin to recede or pull away from the teeth. As this happens, bacteria can enter the space and cause inflammation or infection.
Read on to better understand its causes, symptoms, stages, and treatments.
Causes of Gum Disease
There are a variety of factors that can contribute to periodontal disease. But it all starts with bacteria in plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth.
Plaque can harden into tartar if not removed regularly through brushing and flossing.
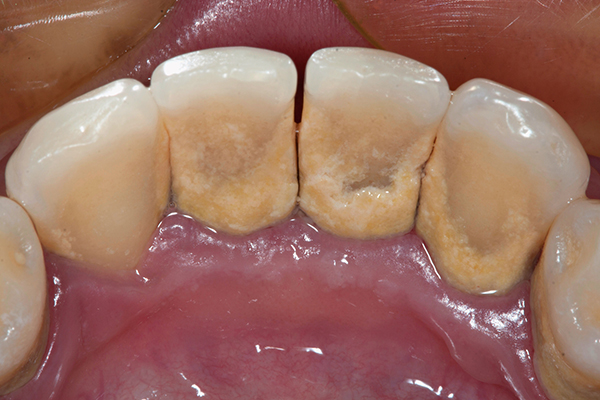
Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, is the primary cause of periodontal disease. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar and increase the risk of gum inflammation and tooth decay.
Other common causes are:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Genetics
- High levels of stress
- Hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy
- Medications that can cause dry mouth
- Certain Health Conditions such as diabetes and HIV
Symptoms of Gum Disease
It can sometimes be hard to recognize gum disease in its early stages. But if you notice any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek treatment right away.
These are the general signs to watch out for
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Receding gum tissue
- Persistent bad breath
- Teeth that look longer than normal due to gum recession
If left untreated, periodontal disease can progress from the early stage of gingivitis to the severe stage known as periodontitis.
See a dentist if
- Chronic bad breath that won’t go away
- Loose teeth or dental abscesses
- Holes or spaces between your teeth
- Pain and swelling in the gums
Ask for an urgent appointment if
- Discomfort when chewing or biting down
- Extreme sensitivity in your teeth and gums
- Fever, nausea, or other signs of infection
Stages of Gum Disease
The stages of gum disease are typically divided into two main categories: gingivitis and periodontitis.
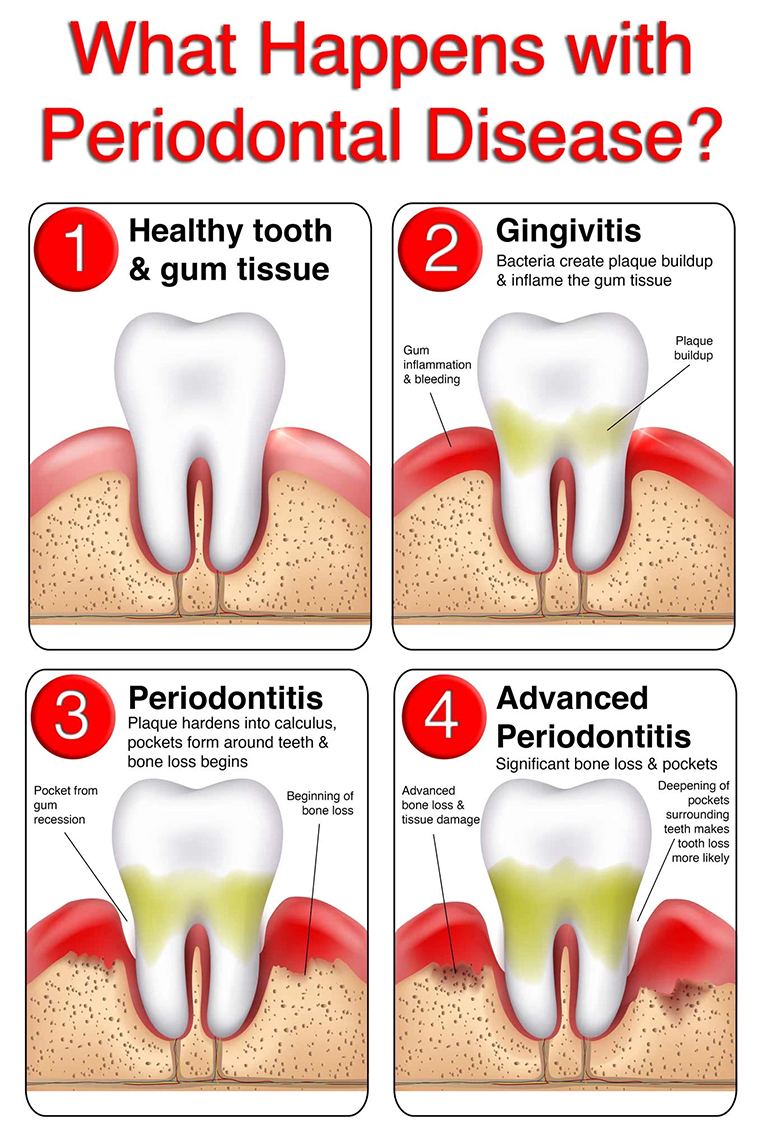
This image illustrates the stages of gum disease, from gingivitis to advanced periodontitis, which can lead to severe damage to the teeth and jawbone and even tooth loss if left untreated.
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, where inflammation or bleeding may occur in response to plaque buildup. Gingivitis can progress to developing periodontitis if left untreated.
Periodontitis is much more severe, characterized by a loss of gum tissue, bone loss around the teeth, and deep pockets forming between the gums and teeth.
Advanced Periodontitis is the most severe stage, where the gums and teeth are severely damaged. At this point, there may be permanent damage to your teeth and jawbone, and tooth loss is possible.
Blyss Dental Tip: Do you have symptoms of gum disease? Schedule a consultation with your dentist right away. Periodontitis becomes more costly to treat as the disease progresses. The natural bone you lose from the disease can’t also be replaced. As you lose bone, your gums start to recede to the point that your teeth may become loose.
Treatments for Gum Disease
Is gum disease curable? Yes! The good news is that there are many treatment options for gum disease, depending on its severity.
At-Home Treatments
The first step for treating gum disease is to improve your oral hygiene habits. This means brushing twice a day, flossing once per day, and visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups.
In addition to this, there are many other at-home treatments that you can try in order to reduce inflammation or infection in the gums.
These include using mouthwashes or rinses, applying an antibiotic ointment to your teeth, and changing your diet to support dental health.
Professional Treatments
If these at-home treatments are not effective in treating gum disease, a dentist may recommend professional treatments.
Non-surgical Treatments
- Scaling and Root Planing (SRP): This treatment, also known as a ‘deep clean,’ involves scraping away the plaque and tartar deposits on teeth below and above the gum line.
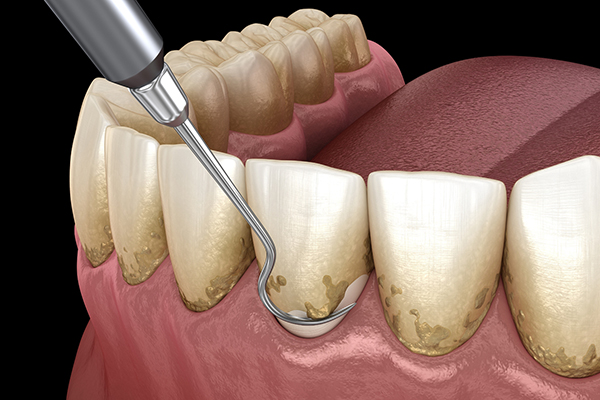
Scaling and Root Planning (SRP) is a deep, comprehensive cleaning procedure where plaque and tartar are removed from underneath the gums to help prevent or treat gum disease and other dental issues.
- Antibiotics: This involves applying medications to the affected gum tissue that helps fight off bacteria and decrease inflammation. These medications may be administered topically or systemically through oral antibiotics or antiseptic mouth rinses.
Surgical Treatments
- Osseous Surgery (Gingival Flap Surgery): This procedure is also called pocket reduction surgery, and it involves making small incisions in the gums in order to lift them back and remove bacterial deposits from underneath them. Once these deposits are removed, sutures are placed in order to help keep the gum tissue firmly attached to the teeth.
- Bone Grafting: During this procedure, either natural or synthetic bone material is inserted into the affected site before being held in place with stitches until eventually fusing with your jawbone after healing is complete.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: The procedure involves taking healthy tissues from another part of your mouth (or sometimes from a donor) and stitching them into place over your receded gum tissue in order to restore a natural look and feel, as well as protect vulnerable roots from decay or damage due to exposure. This is a treatment for receding gums due to periodontal disease.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: Also known as GTR, it is an advanced surgical technique used to regenerate lost gum tissue due to periodontal disease. It involves placing a mesh barrier over affected areas, which helps promote the healthy growth of cells while preventing bacterial growth.
Blyss Dental Tip: In order to prevent and treat gum disease, it is important to maintain good oral health habits. This means brushing your teeth and flossing regularly, as well as visiting the dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Conclusion
Gingivitis and periodontitis are serious dental conditions that can lead to permanent damage if left untreated.
Fortunately, there are many effective treatments available, ranging from at-home remedies to more advanced surgical procedures.
If you think you might have gingivitis or periodontitis, it’s important to seek professional help as soon as possible.
At Blyss Dental, we offer free consultations so that you can get the treatment you need without breaking the bank.
Book a consultation today, and let us help you get on the path to good oral health!
Sources Cited From
- Periodontal Disease | Oral Health Conditions | Division of Oral Health | CDC. (n.d.). https://www.cdc.gov/
oralhealth/ conditions/ periodontal-disease.html - Periodontal (Gum) Disease. (n.d.). National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/
health-info/ gum-disease - Surgical Procedures. (2020, February 5). American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/
for-patients/ periodontal-treatments-and-procedures/ surgical-procedures/ - Oral Health Conditions. (n.d.). https://www.cdc.gov/
oralhealth/ conditions/ index.html - Nazir, M. A. (2017). Prevalence of periodontal disease, its association with systemic diseases and prevention. International Journal of Health Sciences, 11(2), 72-80. https://doi.org/https:/
/www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pmc/articles/ PMC5426403/ - Seitz, M. W. (2019). Current Knowledge on Correlations Between Highly Prevalent Dental Conditions and Chronic Diseases: An Umbrella Review. https://www.cdc.gov/
pcd/ issues/ 2019/ 18_0641.htm - Uwambaye, P. (2021, March 12). Assessing the association between periodontitis and premature birth: a case-control study – BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. BioMed Central. https://bmcpregnancy
childbirth. biomedcentral.com/ articles/ 10.1186/ s12884-021-03700-0